SNOW & ICE
The main goal of these studies is to investigate how mineral dust and black carbon deposition alters the optical properties of Alpine snow and ice. Laboratory equipment, field data, UAV and satellite data are used to characterise the Cryosphere.
It is recently understood that Aeolian-transported light absorbing impurities such as Black Carbon and Mineral Dust have a positive radiative forcing when deposited on snow and ice-covered areas accelerating the melting process. This interaction occurs via a complex mechanism known as snow-albedo feedback. Current investigations rely on the estimation of the concentration of externally mixed impurities in snow by combining field and satellite data.
Main activities regards:
- NEW: Inferring snowmelt and snow properties from thermal inertia (Colombo et al., 2019)
- Development of spectral indices related to the presence of snow impurities (Di Mauro et al., 2015)
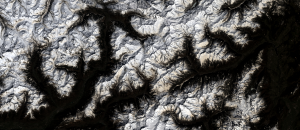
LANDSAT image on Italin Alps showing mineral dust accumulation
- Mapping suitability areas for ice core drilling (Questionnaire on Ice Drilling)
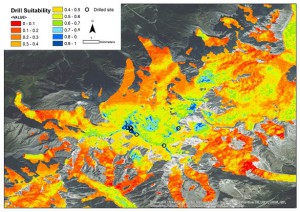
Suitability map of areas for ice core drilling in north western Italian Alps
- Set-up of an ice core spectral system (EuroCold)

Ice core example
6,528 total views, 1 views today
